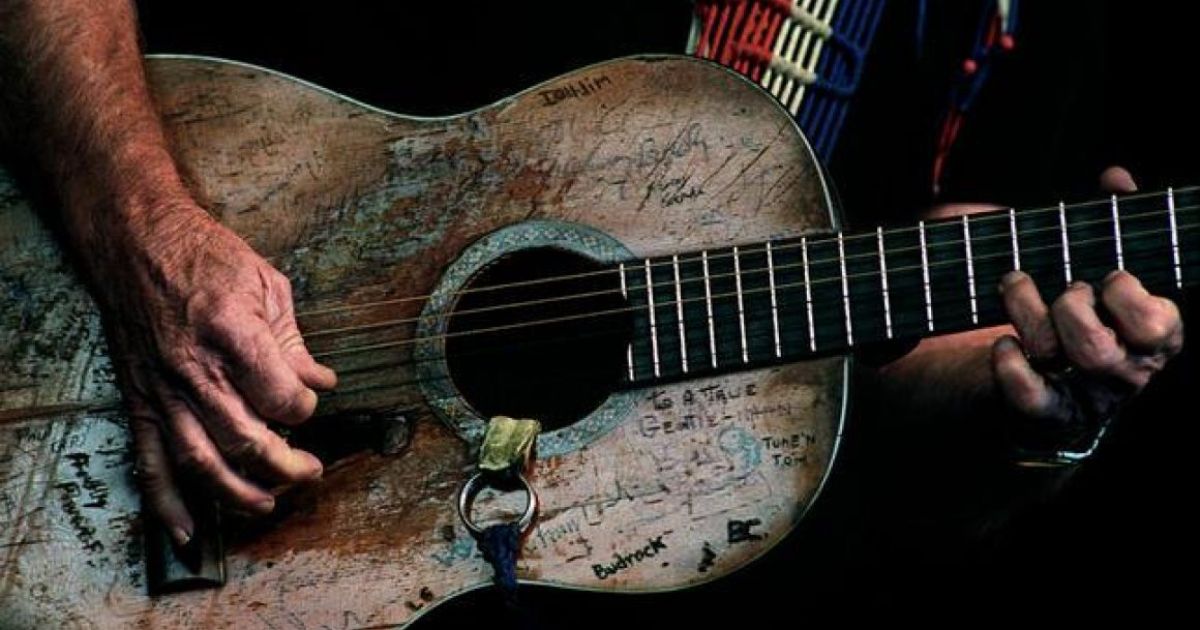
The Oldest Existing Acoustic Guitar refers to the oldest known surviving acoustic guitar in the world. It is a historic musical instrument made without electronic amplification. This guitar has withstood the test of time and is valuable for its age and historical significance in the development of acoustic guitars. It’s a precious relic of musical history.
Uncovering the age of the Oldest Existing Acoustic Guitar is like peeling back the layers of time to reveal a musical treasure. Imagine a musical instrument that has weathered centuries, witnessed historical events, and played a part in the evolution of music. This guitar’s journey through time is a fascinating tale that connects us with the roots of acoustic music. Let’s embark on this remarkable journey together.
To determine the age of the Oldest Existing Acoustic Guitar, experts rely on a combination of historical records, craftsmanship techniques, and scientific analysis. Dating these ancient instruments involves scrutinizing wood types, construction methods, and even examining labels or inscriptions within the guitar. Uncovering its age is like solving a captivating puzzle that helps us better understand the history of music and craftsmanship.
The Birth of the Acoustic Guitar
Early Stringed Instruments
To understand the age of the oldest existing acoustic guitar, we must first examine the early origins of stringed instruments. The concept of plucking strings to create music dates back thousands of years. Ancient civilizations used various forms of stringed instruments, such as the lyre and the lute, which were predecessors to the modern guitar. These instruments provided the foundation for the development of the acoustic guitar.
Medieval and Renaissance Roots
The precursor to the acoustic guitar as we know it today started to take shape during the Middle Ages and the Renaissance. In the early medieval period, instruments like the oud were popular in the Arab world and eventually made their way to Europe through trade and cultural exchanges. These early instruments had a pear-shaped body, round soundhole, and frets on the fingerboard, bearing a striking resemblance to what we now call the acoustic guitar.
The Evolution of the Guitar
The Classical Guitar
The 16th century saw the emergence of the classical guitar, which closely resembled the modern acoustic guitar. It featured six strings and a wooden body, often made from materials like spruce, cedar, or rosewood. Notable luthiers like Antonio Torres Jurado played a significant role in refining the design and construction techniques of these early guitars. The classical guitar gained popularity in Spain and eventually spread throughout Europe.
Steel-String Guitars
While classical guitars continued to evolve, the 19th century witnessed the development of steel-string guitars. These instruments had a brighter and more resonant sound, thanks to their steel strings. The Martin Guitar Company, founded in the 1830s, played a pivotal role in popularizing the steel-string acoustic guitar, setting the stage for the modern acoustic guitar’s dominance.
The Oldest Existing Acoustic Guitars
| Guitar Name | Luthier/Origin | Estimated Age | Notable Features | Current Location |
| Belchior Dias Guitar (1590) | Portuguese luthier | ~ 1590 | Smaller body, nylon strings, Renaissance design | Museum Cité de la Musique, Paris |
| Giovanni Paolo Maggini Guitar | Italian violin maker | ~ 1600 | Flat back, intricate rosette design | Ashmolean Museum, Oxford |
| Gaspard Duiffopruggar Guitar | German luthier | ~ 1590 | Curved bodies, ornate decorations | Various museums and collections |
| Martin & Coupa Guitar (c. 1790) | C.F. Martin and Coupa, Spain | ~ 1790 | Wooden body, steel strings, classic design | Various collectors and museums |
| Louis Panormo Guitar (c. 1840) | British luthier, Italy | ~ 1840 | Transition from classical to steel-string guitars | Collectors and musicians |
Now that we’ve explored the historical context of the acoustic guitar, it’s time to uncover some of the oldest existing examples of this beloved instrument.
Belchior Dias Guitar (1590)
One of the oldest known surviving acoustic guitars is attributed to Belchior Dias, a Portuguese luthier. This guitar, believed to be from around 1590, is a beautiful example of early craftsmanship. It features a smaller body size, nylon strings, and a design reminiscent of the Renaissance-era instruments. It’s housed in the Museum Cité de la Musique in Paris, France, making it a cherished relic of guitar history.
Giovanni Paolo Maggini Guitar (1600)
Giovanni Paolo Maggini, an Italian violin maker, is renowned for his contributions to the world of stringed instruments. While he is more famous for his violins, he also created a few guitars during his lifetime. One of his surviving guitars, dating back to approximately 1600, is an exceptional example of early guitar design. It features a flat back and an intricate rosette design around the soundhole. This rare guitar is part of the collection at the Ashmolean Museum in Oxford, England.
Gaspard Duiffopruggar Guitar (1590)
Gasparo Duiffopruggar, a celebrated luthier from Germany, produced guitars in the late 16th century. His surviving instruments, dating back to around 1590, provide valuable insights into the evolution of the acoustic guitar. These guitars featured elegant and intricate designs, with curved bodies and ornate decorations. A few of his guitars can be found in various museums and private collections.
Martin & Coupa Guitar (c. 1790)
Martin & Coupa is a well-known name among vintage guitar enthusiasts. C.F. Martin, the founder of the renowned Martin Guitar Company, partnered with a Spanish luthier named Coupa to produce high-quality instruments. One of their surviving guitars, created around 1790, is a testament to their craftsmanship. It features a wooden body, steel strings, and a classic design that still influences acoustic guitar makers today.
Louis Panormo Guitar (c. 1840)
Louis Panormo, a British luthier of Italian descent, was a prominent figure in the 19th-century guitar-making scene. His guitars are known for their exceptional craftsmanship and the use of quality materials. One of his guitars, crafted around 1840, showcases the transition from classical to steel-string guitars. This vintage gem is cherished by collectors and musicians alike.
Significance of these Vintage Guitars

The existence of these vintage guitars is not just a matter of historical curiosity; it holds great significance in the world of music and craftsmanship.
Historical Insights
Vintage guitars like those mentioned above provide us with invaluable insights into the evolution of the acoustic guitar. They offer a tangible link to the past, helping us understand the design, materials, and techniques used by luthiers in different eras. This knowledge is crucial for preserving and advancing the art of guitar making.
Musical Legacy
These guitars are more than just relics; they are playable instruments that have withstood the test of time. Musicians, collectors, and historians cherish the opportunity to play and hear the sounds of these vintage guitars, connecting them to the music of the past. Many contemporary musicians seek out vintage instruments to capture the unique tonal qualities and character that older guitars possess.
Inspiration for Modern Luthiers
The craftsmanship and artistry of these vintage guitars continue to inspire modern luthiers and guitar makers. Studying the construction techniques and design choices of these old instruments helps contemporary builders improve their skills and create instruments that pay homage to the past while meeting the demands of today’s musicians.
Challenges of Preserving Vintage Guitars
Preserving these antique guitars comes with its own set of challenges. Time, environmental factors, and the hands of countless owners can take a toll on these delicate instruments.
Wood Aging and Damage
Wood, the primary material in guitar construction, can change over time. It can warp, crack, or suffer from insect damage if not stored and maintained properly. Restoring vintage guitars while preserving their historical integrity is a delicate and often complex process.
String and Fretboard Wear
The constant pressure and vibration of strings can wear down the frets and fingerboard over time. The choice of strings, string tension, and playing style can all affect the condition of the fretboard. Restoring these components requires a skilled hand and attention to detail.
Climate and Humidity Control
Guitars are sensitive to changes in humidity and temperature. Vintage guitars, in particular, require a stable environment to prevent damage. Museums and collectors invest in climate control systems to maintain ideal conditions for these historical instruments.
Collecting and Valuing Vintage Guitars
The world of vintage guitar collecting is a passionate and often lucrative endeavor. Collectors and enthusiasts carefully evaluate the age, condition, rarity, and historical significance of a guitar when determining its value.
Age
The age of a guitar is a significant factor in its value. Generally, the older the guitar, the more valuable it is, especially if it’s in good condition and playable. Guitars from the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries are highly sought after.
Condition
The condition of a vintage guitar is critical. Guitars that have been well-preserved and maintained over the years are more desirable. Originality, including the presence of original parts and finish, also plays a crucial role in determining a guitar’s value.
Rarity
Some vintage guitars are more valuable due to their rarity. Limited production runs, unique designs, and historical significance can make a guitar extremely rare and, therefore, highly sought after by collectors.
Provenance
The history of a guitar, including its previous owners and any famous musicians associated with it, can significantly affect its value. A guitar with a compelling backstory can command a premium price.
Historical Significance
Guitars that played a crucial role in the history of music, such as instruments used by famous musicians or luthiers, are highly prized. These guitars often find their way into museums and private collections.
Famous Musicians and Their Vintage Guitars
Vintage guitars have been played by some of the most iconic musicians in history. Let’s explore a few famous artists and their beloved vintage instruments.
Eric Clapton’s Blackie
Eric Clapton is one of the most influential guitarists of all time. His Blackie is a vintage Fender Stratocaster, pieced together from several vintage Strats he acquired in the 1970s. Blackie’s combination of vintage parts and Clapton’s exceptional skill made it one of the most famous guitars in rock history.
Jimi Hendrix’s Monterey Pop Festival Stratocaster
Jimi Hendrix’s performance at the Monterey Pop Festival in 1967 is legendary. He famously set fire to his Fender Stratocaster at the end of his set. The guitar was later restored and is now a cherished vintage piece that symbolizes the iconic moment in rock history.
Bob Dylan’s 1964 Gibson
Bob Dylan’s 1964 Gibson acoustic guitar is celebrated for its role in his early folk and protest songs. Its distinct tone and Dylan’s timeless lyrics made it an iconic instrument in the world of music.
Stevie Ray Vaughan’s Lenny
Stevie Ray Vaughan’s “Lenny” is a 1965 Fender Stratocaster that he named after his wife. The guitar’s unique history and Vaughan’s exceptional blues-playing skills have made it a legendary vintage instrument.
The Enduring Appeal of Vintage Guitars
Vintage guitars continue to captivate musicians and collectors alike, and their enduring appeal can be attributed to several factors.
Unique Tonality
Vintage guitars often possess a distinct tonal quality that sets them apart from modern instruments. The aging of wood, the use of different materials, and the craftsmanship of a bygone era contribute to a unique and desirable sound.
Historical Connection
Owning a vintage guitar connects musicians and collectors to the history of music. Playing an instrument that has been a part of the music world for decades or even centuries can be a profound and inspiring experience.
Investment Potential
While the primary motivation for owning a vintage guitar is often the love of music and craftsmanship, these instruments can also be valuable investments. The value of vintage guitars tends to appreciate over time, making them a sound financial choice for collectors.
Artistry and Craftsmanship
The meticulous craftsmanship that went into the creation of vintage guitars is a testament to the skills of luthiers from the past. The attention to detail, choice of materials, and design sensibilities make vintage guitars works of art as well as musical instruments.
Preserving Vintage Guitars for Future Generations
Preserving vintage guitars and understanding the Difference Between Classical And Acoustic Guitar is not just a responsibility of collectors and museums; it’s a shared commitment to safeguarding our musical heritage. Here are some measures that can be taken to ensure these treasures are passed onto future generations.
Proper Storage and Care
Storing vintage guitars in controlled environments with stable humidity and temperature levels is crucial. Regular maintenance, including restringing, cleaning, and minor repairs, can help prevent further damage.
Documentation
Maintaining detailed records of a guitar’s history and provenance is essential. This documentation can prove the authenticity and historical significance of the instrument.
Conservation Efforts
Museums and institutions that house vintage guitars invest in conservation efforts to protect these instruments. Conservationists work to stabilize and restore guitars when necessary while preserving their historical integrity.
Public Access
Making vintage guitars accessible to the public through exhibitions and educational programs is a way to share their historical and musical significance. Museums and collections play a vital role in this effort.
FAQs
How old is the oldest acoustic guitar?
The oldest known acoustic guitar is around 400 years old.
How do experts determine its age?
Experts use clues like wood type and craftsmanship techniques, along with historical records, to estimate its age.
Why is it important to know the age of the oldest acoustic guitar?
Knowing its age helps us trace the history of music and craftsmanship, connecting us to the past.
Conclusion
The quest to determine the age of the Oldest Existing Acoustic Guitar is a fascinating journey that unearths the rich history of this iconic musical instrument. Using a combination of historical research, craftsmanship analysis, and scientific methods, experts can estimate the age of these ancient guitars. This knowledge not only satisfies our curiosity but also deepens our appreciation for the artistry and evolution of guitar-making.
Discovering the age of the oldest acoustic guitar is like connecting with the musical past, tracing the footsteps of generations of musicians and artisans. It reminds us that even in the ever-changing world of music, there are timeless treasures that continue to resonate with the beauty of bygone eras. Whether displayed in museums or cherished in private collections, these guitars serve as a testament to the enduring legacy of the acoustic guitar, allowing us to appreciate its role in shaping the melodious tapestry of our musical history.